Hi, today we'll learn about the elements and attributes used in HTML 5 so lets start from Elements:
HTML uses Elements to describe the Structure of pages, lets look closer at the code from the last lecture, there are several different Elements. each Element has opening tag and a closing tag.
Tags
tags act like containers. they tell you something about the information between their opening and closing tags.
*The opening <html> tag indicates that anything between it and a closing </html> tag is HTML code.
The <body> tag indicates that anything between it and the closing
</body> tag should be shown inside the main browser window.
Words between <h1> and </h1> are a main heading.
A paragraph of text appears between these <p> and </p> tags.
Words between <h2> and </h2> form a sub-heading.
Here is another paragraph between opening <p> and closing </p> tags.
Another sub-heading inside <h2> and </h2> tags.
Another paragraph inside <p> and </p> tags.
The closing </body> tag indicates the end of what should appear in the main browser
window.
The closing </html> tag indicates that it is the end of the HTML code.
Attributes tell us more about Elements
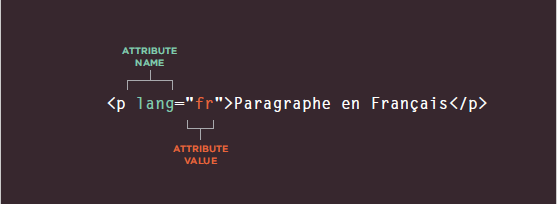
Attributes provide additional information about the contents of an element. They appear on the opening tag of the element and are made up of two parts:
a name and a value, separated by an equals sign.
-The attribute name indicates what kind of extra information you are supplying about the
element's content. It should be written in lowercase.
-The value is the information or setting for the attribute. It should be placed in double quotes. Different attributes can have different values.
-Here an attribute called lang is used to indicate the language used in this element. The value of this attribute on this page specifies it is in US English.
*The majority of attributes can only be used on certain
elements, although a few
attributes (such as lang) can appear on any element.
-Most attribute values are either pre-defined or follow a stipulated format. We will look at the permitted values as we introduce each new attribute. The value of the lang attribute is an abbreviated way of specifying which language is used inside the element that all browsers understand.
BODY, HEAD & TITLE
<body>
-You met the <body> element in the first example we created. Everything inside this element is shown inside the main browser window.
<head>
-Before the <body> element you will often see a <head> element. This contains information
about the page (rather than information that is shown within the main part of the browser
window that is highlighted in blue on the opposite page). You will usually find a <title>
element inside the <head> element.
<title>
-The contents of the <title> element are either shown in the top of the browser, above where
you usually type in the URL of the page you want to visit, or on the tab for that page (if your
browser uses tabs to allow you to view multiple pages at the same time).
You may know that HTML stands for (Hyper Text Markup Language) The Hyper Text part
refers to the fact that HTML allows you to create links that allow visitors to move from one
page to another quickly and easily, a markup language allows you to annotate text and these annotations provide additional meaning to the contents of a document. If you think of a web page we add code around the original text we want to display and the browser then uses the code to display the page correctly So the tags we add are the markup.
NOTE: ( keep practicing the code, try to change the headings )
HTML uses Elements to describe the Structure of pages, lets look closer at the code from the last lecture, there are several different Elements. each Element has opening tag and a closing tag.
Tags
tags act like containers. they tell you something about the information between their opening and closing tags.
*The opening <html> tag indicates that anything between it and a closing </html> tag is HTML code.
The <body> tag indicates that anything between it and the closing
</body> tag should be shown inside the main browser window.
Words between <h1> and </h1> are a main heading.
A paragraph of text appears between these <p> and </p> tags.
Words between <h2> and </h2> form a sub-heading.
Here is another paragraph between opening <p> and closing </p> tags.
Another sub-heading inside <h2> and </h2> tags.
Another paragraph inside <p> and </p> tags.
The closing </body> tag indicates the end of what should appear in the main browser
window.
The closing </html> tag indicates that it is the end of the HTML code.
Attributes tell us more about Elements
Attributes provide additional information about the contents of an element. They appear on the opening tag of the element and are made up of two parts:
a name and a value, separated by an equals sign.
-The attribute name indicates what kind of extra information you are supplying about the
element's content. It should be written in lowercase.
-The value is the information or setting for the attribute. It should be placed in double quotes. Different attributes can have different values.
-Here an attribute called lang is used to indicate the language used in this element. The value of this attribute on this page specifies it is in US English.
*The majority of attributes can only be used on certain
elements, although a few
attributes (such as lang) can appear on any element.
-Most attribute values are either pre-defined or follow a stipulated format. We will look at the permitted values as we introduce each new attribute. The value of the lang attribute is an abbreviated way of specifying which language is used inside the element that all browsers understand.
BODY, HEAD & TITLE
<body>
-You met the <body> element in the first example we created. Everything inside this element is shown inside the main browser window.
<head>
-Before the <body> element you will often see a <head> element. This contains information
about the page (rather than information that is shown within the main part of the browser
window that is highlighted in blue on the opposite page). You will usually find a <title>
element inside the <head> element.
<title>
-The contents of the <title> element are either shown in the top of the browser, above where
you usually type in the URL of the page you want to visit, or on the tab for that page (if your
browser uses tabs to allow you to view multiple pages at the same time).
You may know that HTML stands for (Hyper Text Markup Language) The Hyper Text part
refers to the fact that HTML allows you to create links that allow visitors to move from one
page to another quickly and easily, a markup language allows you to annotate text and these annotations provide additional meaning to the contents of a document. If you think of a web page we add code around the original text we want to display and the browser then uses the code to display the page correctly So the tags we add are the markup.
NOTE: ( keep practicing the code, try to change the headings )



Comments
Post a Comment