Hi, today we'll going to learn about Software requirements, specifications, applications and lots of more let's start with software engineering definition.
Software Engineering
-Software engineering is an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production form the early stages of system specification through to maintaining the system after it has gone into use.
-The economies of all developed nations are dependent on software.
-More and more systems are software controlled software engineering is concerned with theories, methods and tools for professional software development.
-Expenditure on software represents a significant fraction of GNP in all developed countries.
-Engineering discipline:
Using appropriate theories and methods to solve problems bearing in mind organizational and financial constraints.
-All aspects of software productions:
Not just technical process of development also project management and the development
of tools methods etc. to support software production.
Software Products
There are two types of software products: Generic and Customized products.
-Generic Products:
Stand alone systems that are marketed and sold to any customer who wishes to buy them.
Examples - PC software such as graphics programs, project management tools, CAD software, software for specific markets such as appointments systems for dentists.
-Specifications of Generic Products:
the specifications of what the software should do is owned by the software developer and decisions on software change are made by the developer.
-Specifications of Customization Products:
The specification of what the software should do is owned by the customer for the software, and they make decisions on software changes that are required.
-Customized Products:
Software that is commissioned by a specific customer to meet their own needs.
Examples - Embedded control system, air traffic control software, traffic monitoring systems.
General issues that affect most software
-Heterogeneity:
Increasingly systems are required to operate as distributed systems across networks that include different types of computer and mobile devices.
-Business and social change:
Business and society are changing incredibly quickly as emerging economies develop and new technologies become available, they need to be able to change their existing software to rapidly develop new software.
-Security and trust:
As software is intertwined with all aspects of our lives it is essential that we can trust that software.
APPLICATION TYPES
-Stand-Alone Applications:
These are applications systems that run on a local computer such as a PC, they include all necessary functionality and do not need to be connected to a internet network or any network.
-Interactive transaction based applications:
Applications that execute on a remote computer and are accessed by user form their own PCs or terminals, these include web applications such as e-commerce applications.
-Embedded Control Systems:
These are software control systems that control and manage hardware devices. numerically, there are probably more embedded systems then any other type of system.
-Batch Processing systems:
These are business systems that are designed to process data in large batches. they process large numbers of individual inputs to create corresponding outputs.
-Entertainment Systems:
These are systems that are primarily for personal use and which are intended to entertain the user e.g video and mp3 players.
-Systems for modeling and simulation:
These are systems that are developed by scientists and engineers to model physical process or situations which include many separate interacting objects.
Web Based Software Engineering
Web based systems are complex distributed systems but the fundamentals principles of software engineering discussed previously are as applicable to them as they are apply to web based software in the same way that they apply to other types of software system or to any other types of system.
Note: (read about software models in software engineering)
Software Engineering
-Software engineering is an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production form the early stages of system specification through to maintaining the system after it has gone into use.
-The economies of all developed nations are dependent on software.
-More and more systems are software controlled software engineering is concerned with theories, methods and tools for professional software development.
-Expenditure on software represents a significant fraction of GNP in all developed countries.
-Engineering discipline:
Using appropriate theories and methods to solve problems bearing in mind organizational and financial constraints.
-All aspects of software productions:
Not just technical process of development also project management and the development
of tools methods etc. to support software production.
 |
| These are the questions and answers you have to know |
Software Products
There are two types of software products: Generic and Customized products.
-Generic Products:
Stand alone systems that are marketed and sold to any customer who wishes to buy them.
Examples - PC software such as graphics programs, project management tools, CAD software, software for specific markets such as appointments systems for dentists.
-Specifications of Generic Products:
the specifications of what the software should do is owned by the software developer and decisions on software change are made by the developer.
-Specifications of Customization Products:
The specification of what the software should do is owned by the customer for the software, and they make decisions on software changes that are required.
-Customized Products:
Software that is commissioned by a specific customer to meet their own needs.
Examples - Embedded control system, air traffic control software, traffic monitoring systems.
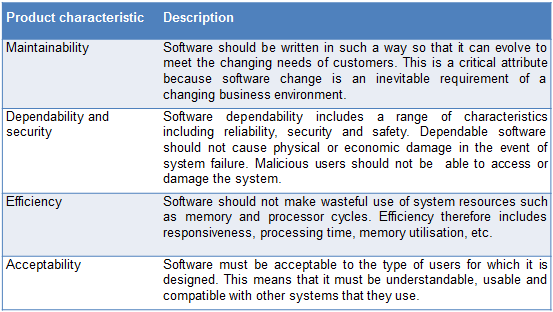 |
| Essential Attributes of a good software |
General issues that affect most software
-Heterogeneity:
Increasingly systems are required to operate as distributed systems across networks that include different types of computer and mobile devices.
-Business and social change:
Business and society are changing incredibly quickly as emerging economies develop and new technologies become available, they need to be able to change their existing software to rapidly develop new software.
-Security and trust:
As software is intertwined with all aspects of our lives it is essential that we can trust that software.
APPLICATION TYPES
-Stand-Alone Applications:
These are applications systems that run on a local computer such as a PC, they include all necessary functionality and do not need to be connected to a internet network or any network.
-Interactive transaction based applications:
Applications that execute on a remote computer and are accessed by user form their own PCs or terminals, these include web applications such as e-commerce applications.
-Embedded Control Systems:
These are software control systems that control and manage hardware devices. numerically, there are probably more embedded systems then any other type of system.
-Batch Processing systems:
These are business systems that are designed to process data in large batches. they process large numbers of individual inputs to create corresponding outputs.
-Entertainment Systems:
These are systems that are primarily for personal use and which are intended to entertain the user e.g video and mp3 players.
-Systems for modeling and simulation:
These are systems that are developed by scientists and engineers to model physical process or situations which include many separate interacting objects.
Web Based Software Engineering
Web based systems are complex distributed systems but the fundamentals principles of software engineering discussed previously are as applicable to them as they are apply to web based software in the same way that they apply to other types of software system or to any other types of system.
Note: (read about software models in software engineering)
Comments
Post a Comment